3 网络模块
# 3 网络模块
主要用于构建深度学习模型。
参数理解: 假设你的数据集包含32个句子,每个句子的长度不超过10个单词,每个单词用100维的词嵌入向量表示。那么,你的输入数据的形状(tensor形状)就是:
(batch_size, input_length(sequence_length), input_size) = (32, 10, 100)
1
| 参数名 | 含义 | 全称 | 典型用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
N | 批大小 | Batch size | 一次处理的数据样本数量 |
Cin | 输入通道数 | Channels in | 输入特征的通道数,例如 RGB 图像是 3 |
Cout | 输出通道数 | Channels out | 网络输出的通道数,通常是卷积核数量 |
Hin | 输入高度 | Height in | 图像或特征图的垂直维度 |
Win | 输入宽度 | Width in | 图像或特征图的水平维度 |
Hout | 输出高度 | Height out | 经过网络后的垂直维度 |
Wout | 输出宽度 | Width out | 经过网络后的水平维度 |
Lin | 输入序列长度 | Length in | 序列的时间步或长度,常用于 RNN/LSTM |
Lout | 输出序列长度 | Length out | LSTM 输出序列的长度(通常等于 Lin) |
D | 特征维度 | Dim | 每个时间步或样本的特征维数(用于 LSTM) |
# 3.1 Torch.nn使用
# nn.Linear()
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Linear.html

import torch
from torch import nn
linear = torch.nn.Linear(in_features=64, out_features=3)
input = torch.rand(10,64)
output = linear(input)
print(output)
print(output.shape) # 10*3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
tensor([[-0.0043, -0.3533, 0.7606],
[-0.2995, 0.1500, 0.7348],
[-0.2207, -0.4110, 0.7303],
[ 0.1700, -0.0216, 0.4602],
[-0.3685, -0.1015, 0.4496],
[-0.1225, -0.0397, 0.8009],
[ 0.0735, -0.0215, 0.7582],
[-0.1960, -0.0924, 0.5687],
[-0.1162, -0.2948, 0.5116],
[-0.4587, -0.2869, 0.5024]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
torch.Size([10, 3])
# nn.Conv1d()
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv1d.html

其中:


conv1 = nn.Conv1d(in_channels=256, out_channels=10, kernel_size=2, stride=1, padding=0)
input = torch.randn(32,32,256)
# 发现Cin != in_channels,修正
input_new = input.permute(0,2,1)
out = conv1(input_new)
print(out.shape) # 31=(32+2*0-1*1-1)/1+1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
torch.Size([32, 10, 31])
# nn.RNN
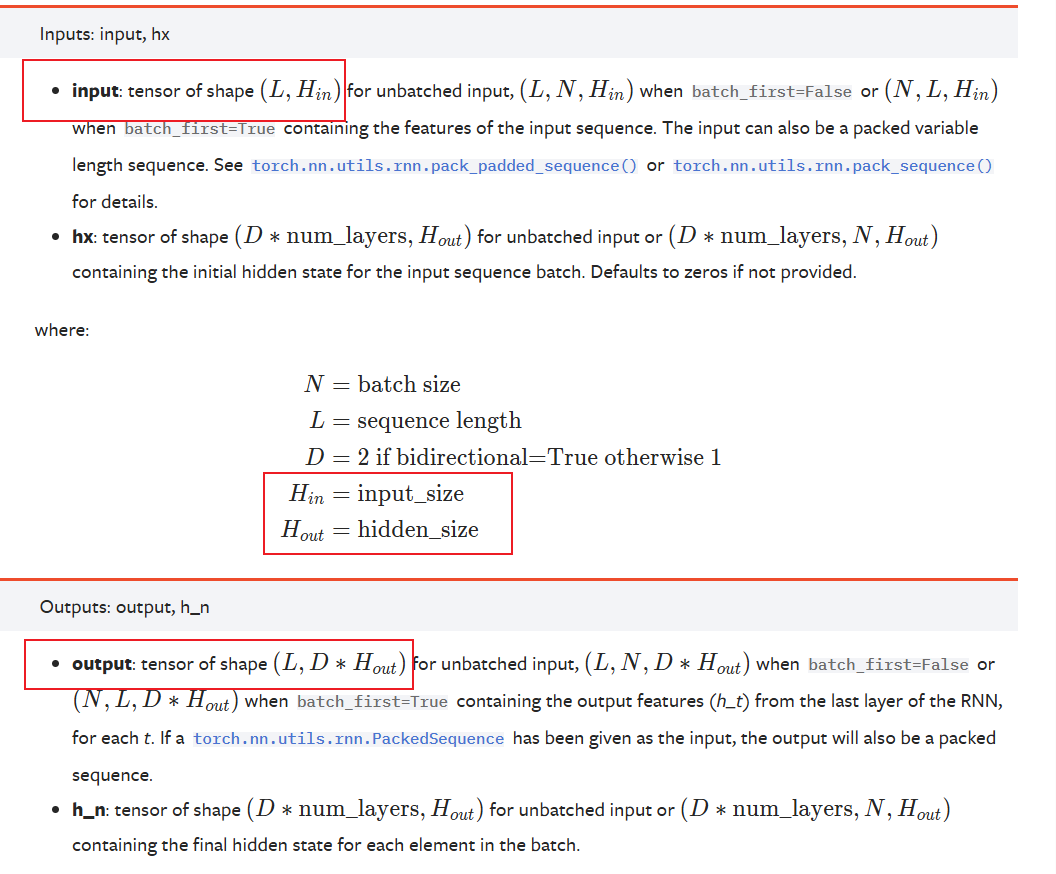
import torch
from torch import nn
num_steps = 35
batch_size = 2
feature_size = 32
num_hiddens = 2
x = torch.rand(num_steps, batch_size, feature_size)
RNN_X = nn.RNN(input_size=feature_size, hidden_size=num_hiddens)
y, state_new = RNN_X(x)
print(x.shape, y.shape)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
torch.Size([35, 2, 32]) torch.Size([35, 2, 2])
# 3.2 自建深度学习类
使用torch.nn.Module作为父类,重点重写__init__、forward方法
# init()
常用于模型参数初始化
# forward()
常用于厘清数据流动关系
# 示例代码:
import torch
from torch import nn
class MyNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyNet, self).__init__() # 使用父类的方法初始化子类
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(96, 1024) # [96,1024]
self.relu1 = torch.nn.ReLU(True)
self.batchnorm1d_1 = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(1024)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(1024, 7 * 7 * 128) # [1024,6272]
self.relu2 = torch.nn.ReLU(True)
self.batchnorm1d_2 = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(7 * 7 * 128)
self.ConvTranspose2d = nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 4, 2, padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.relu1(x)
x = self.batchnorm1d_1(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
x = self.relu2(x)
x = self.batchnorm1d_2(x)
x = self.ConvTranspose2d(x)
return x
model = MyNet()
print(model)
# 运行结果为:
# MyNet(
# (linear1): Linear(in_features=96, out_features=1024, bias=True)
# (relu1): ReLU(inplace=True)
# (batchnorm1d_1): BatchNorm1d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
# (linear2): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=6272, bias=True)
# (relu2): ReLU(inplace=True)
# (batchnorm1d_2): BatchNorm1d(6272, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
# (ConvTranspose2d): ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1))
# )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
MyNet(
(linear1): Linear(in_features=96, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(relu1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(batchnorm1d_1): BatchNorm1d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(linear2): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=6272, bias=True)
(relu2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(batchnorm1d_2): BatchNorm1d(6272, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(ConvTranspose2d): ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1))
)
# 3.3 模型类的使用
构造函数有无参数
